Causes and Contributing Factors
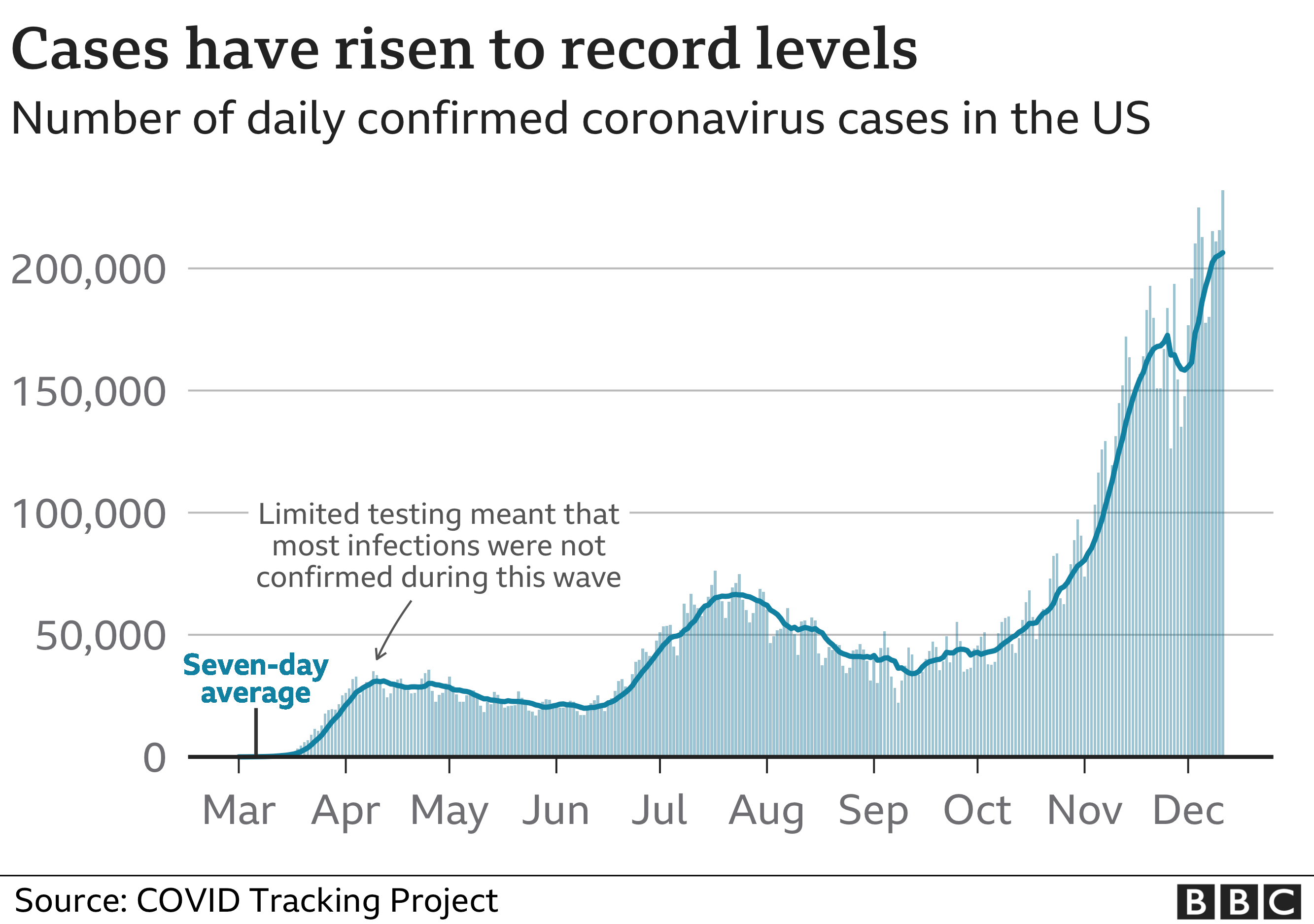
COVID-19 surges are characterized by a rapid increase in new cases, hospitalizations, and deaths. Understanding the factors that contribute to these surges is crucial for implementing effective public health interventions and mitigating their impact.
New Variants
The emergence of new variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is a significant driver of surges. These variants can possess mutations that enhance their transmissibility, severity, or ability to evade the immune system. For instance, the Delta variant, which emerged in late 2020, was significantly more transmissible than earlier strains, leading to widespread surges globally. Similarly, the Omicron variant, identified in late 2021, exhibited even higher transmissibility and was able to partially evade vaccine-induced immunity, contributing to substantial surges in many countries.
Seasonal Trends, Covid surge
Seasonal changes can influence COVID-19 transmission patterns. During the colder months, people tend to spend more time indoors, increasing the likelihood of close contact and virus spread. Additionally, lower humidity and colder temperatures may favor virus survival. Studies have observed seasonal peaks in COVID-19 cases, particularly during winter, suggesting that seasonal factors can contribute to surges.
Vaccination Rates
Vaccination rates play a crucial role in mitigating the severity of COVID-19 surges. Higher vaccination coverage within a population generally leads to reduced transmission and hospitalization rates, thereby lessening the impact of surges. Conversely, lower vaccination rates, particularly among vulnerable populations, can contribute to more severe surges.
Behavioral Changes
Changes in human behavior, such as social distancing, mask-wearing, and travel patterns, can significantly influence COVID-19 transmission. Relaxing these measures, particularly during periods of low case numbers, can lead to a resurgence of the virus. Conversely, maintaining strict adherence to public health guidelines can help suppress transmission and prevent surges.
Healthcare System Capacity
The capacity of healthcare systems to manage surges is a critical factor in determining the severity of their impact. During surges, hospitals and healthcare facilities can become overwhelmed, leading to delays in care, increased mortality rates, and potential strain on medical resources. Effective surge management requires adequate hospital beds, medical staff, and supplies, as well as strategies to optimize resource allocation and minimize strain on the healthcare system.
Mitigation Strategies and Responses: Covid Surge

COVID-19 surges have posed significant challenges to global health systems and economies. To effectively manage these surges, a multifaceted approach encompassing public health measures, vaccination, treatment, healthcare system preparedness, and government policies is crucial.
Public Health Measures
Public health measures have played a pivotal role in mitigating the spread of COVID-19. These measures aim to reduce transmission by limiting close contact and encouraging hygiene practices.
- Mask Mandates: Mask mandates have been widely implemented to reduce the spread of respiratory droplets, which can carry the virus. Studies have shown that mask-wearing significantly reduces transmission rates, particularly in settings with high viral loads. For instance, a study published in the journal “Nature” found that mask mandates in the United States were associated with a substantial reduction in COVID-19 cases and deaths.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining physical distance between individuals is another key strategy to minimize contact and reduce the risk of transmission. Social distancing measures, such as limiting gatherings and encouraging remote work, have been shown to effectively slow the spread of the virus.
- Testing: Widespread testing is essential for identifying infected individuals and isolating them to prevent further transmission. Regular testing, particularly in high-risk settings, can help to detect cases early and facilitate timely intervention. For example, widespread testing programs in South Korea and Germany have been credited with helping to contain the spread of COVID-19.
Vaccination and Boosters
Vaccination is a cornerstone of COVID-19 mitigation strategies. Vaccines have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19.
- Vaccination Programs: Mass vaccination programs have been crucial in reducing the severity of COVID-19 surges. Countries with high vaccination rates have generally experienced less severe surges, with lower hospitalization and mortality rates. For instance, Israel’s aggressive vaccination campaign has been highly effective in reducing COVID-19 cases and deaths.
- Booster Doses: Booster doses have been shown to enhance immunity and provide additional protection against COVID-19, particularly against emerging variants. Booster programs have been implemented in many countries to maintain high levels of population immunity. Studies have demonstrated that booster doses significantly increase antibody levels and reduce the risk of breakthrough infections.
Treatment and Therapeutics
Antiviral medications and other treatments have been developed to manage COVID-19 infection. These treatments aim to reduce the severity of illness and improve patient outcomes.
- Antiviral Medications: Antiviral medications, such as Paxlovid and remdesivir, have been shown to reduce the duration of symptoms and the risk of hospitalization in high-risk individuals. These medications work by interfering with the virus’s ability to replicate, thereby reducing its impact on the body.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-made proteins that can bind to the virus and block its entry into cells. They have been used to treat COVID-19 in high-risk individuals, particularly those with mild to moderate illness.
- Other Treatments: Other treatments, such as corticosteroids and oxygen therapy, are used to manage symptoms and support lung function in severe cases of COVID-19.
Healthcare System Preparedness
A robust healthcare system is essential for managing COVID-19 surges. This includes ensuring adequate hospital capacity, staffing, and resources to effectively care for patients.
- Hospital Capacity: Increasing hospital bed capacity, including ICU beds, is crucial to handle surges in patient admissions. This can involve expanding existing facilities, converting other areas into temporary hospital units, or establishing field hospitals.
- Staffing: Ensuring sufficient medical staff, including nurses, doctors, and respiratory therapists, is critical for providing quality care to COVID-19 patients. This may involve recruiting additional staff, redeploying existing staff, or utilizing telehealth technologies to expand access to care.
- Resources: Adequate supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilators, medications, and other medical resources are essential for effective patient management. This requires robust supply chains and strategic planning to ensure availability during surges.
Government Policies and Interventions
Government policies and interventions play a critical role in controlling COVID-19 surges. These policies can include public health measures, vaccination programs, financial support for businesses and individuals, and travel restrictions.
- Public Health Measures: Governments have implemented a range of public health measures, such as mask mandates, social distancing guidelines, and testing programs, to reduce transmission. The effectiveness of these measures can vary depending on factors such as compliance, enforcement, and the specific context.
- Vaccination Programs: Governments have been instrumental in promoting and facilitating vaccination programs. This includes procuring vaccines, establishing vaccination centers, and implementing public awareness campaigns.
- Financial Support: Governments have provided financial assistance to businesses and individuals affected by COVID-19, such as unemployment benefits, business loans, and rent relief. These measures aim to mitigate the economic impact of the pandemic and support recovery.
- Travel Restrictions: Travel restrictions have been implemented to limit the spread of COVID-19 across borders. These restrictions can include quarantine requirements, testing mandates, and bans on travel from specific countries. The effectiveness of travel restrictions can depend on factors such as the level of international cooperation and the ability to effectively enforce measures.
Covid surge lagi naik, duh! Stress banget sih, tapi kita harus tetap jaga imun. Ngomongin imun, inget kasus di Iran dan Israel , mereka kan lagi perang dingin. Gimana ya caranya supaya mereka bisa damai dan fokus jaga kesehatan masing-masing, biar covidnya gak makin parah?
Covid surge lagi naik, bikin semua orang panik. Tapi tenang, ada solusinya! Nggak usah khawatir, mendingan rileks dulu, sambil nikmatin minuman dingin kayak Wendy Frosty yang seger banget. Habis itu, baru deh kita pikirin lagi cara ngatasin covid ini bareng-bareng.